
The Financial Independence, Retire Early (F.I.R.E) movement has inspired many to rethink money, time, and freedom. Its promise is straightforward: achieve financial independence early so you can focus on what really matters.
While the idea started in the U.S., its principles are being adapted in India, where inflation, rising rents, and cultural values make the journey to financial freedom different. At the heart of this journey is one often-overlooked asset: your home.
Globally, the F.I.R.E model emphasizes three basics: save aggressively, invest consistently, and cut ongoing expenses. In India, the framework shifts slightly.
With limited pension options, rising healthcare costs, and fluctuating rent, real estate plays a much bigger role in wealth creation. According to the RBI Household Finance Committee Report, about 70% of Indian household wealth is in real estate, compared to just 11% in financial assets.
For many Indian families, this isn’t by chance. It reflects both emotional security and sound financial planning. A home is not just a place to live; it is the foundation of long-term independence.
Owning a home doesn’t just affect finances; it also influences behavior.
Studies in behavioral finance show that once a family owns its primary residence, it tends to develop better saving habits. With rent uncertainty gone, financial planning becomes more focused on long-term goals.
A 2023 HSBC study found that Indian homeowners save about 28% more each month than renters with similar incomes. The reason is clear: rent is an expense that disappears each month, while EMIs gradually turn cash outflows into ownership and stability.
This change from “spending to live” to “investing to own” often marks the first silent step toward financial independence.
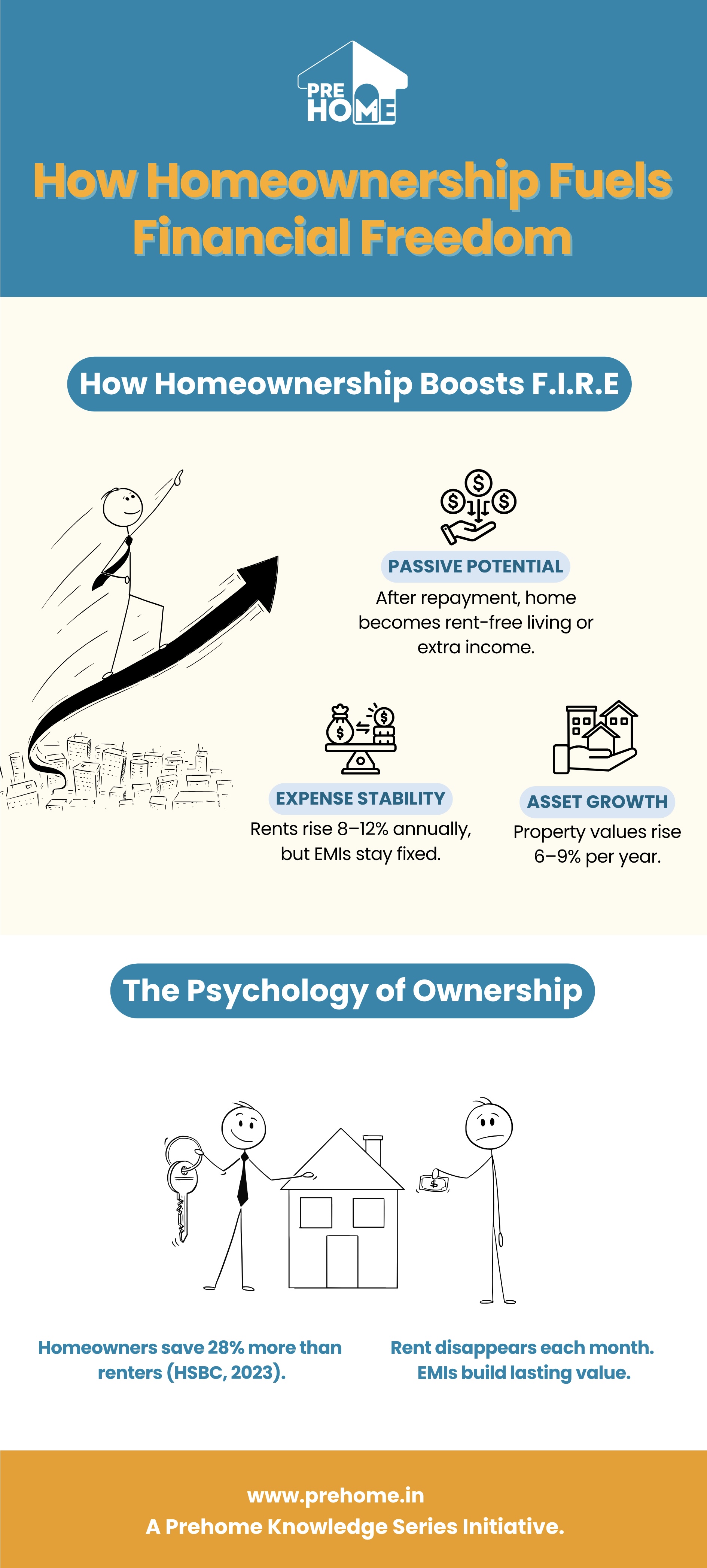
To achieve financial independence, three key factors matter most: asset growth, expense stability, and passive potential. Owning a home quietly supports all three.
Think about this: a homeowner who locks in a ₹60 lakh apartment today with a ₹55,000 monthly EMI could save over ₹1.1 crore in rent over 25 years, even before considering price appreciation.
Each EMI payment builds ownership quietly—part of it reduces your loan, while the rest increases with your property’s value. Over time, this creates home equity, an asset that can later be used, monetized, or repurposed for financial independence. This idea of turning debt into equity and equity into opportunity is key to the F.I.R.E journey in India. In our next blog, “The Equity Engine” we will look at how to speed up this process through better repayment, prepayment, and loan structuring strategies.
Financial independence isn’t reached by taking shortcuts or making high-risk bets. It comes from thoughtful ownership—of your time, money, and eventually, your home.
As we discussed previously about NRI Property Divestment, preserving wealth depends on structure and foresight. Here, we move from preserving wealth to creating it by treating your home as your most valuable financial partner.
In our next piece, we will explore how homeownership grows over time and how small, consistent choices can turn your home into the base for early retirement.